Benefits of Variable-Speed Hydronic Heat Pumps for Contractors
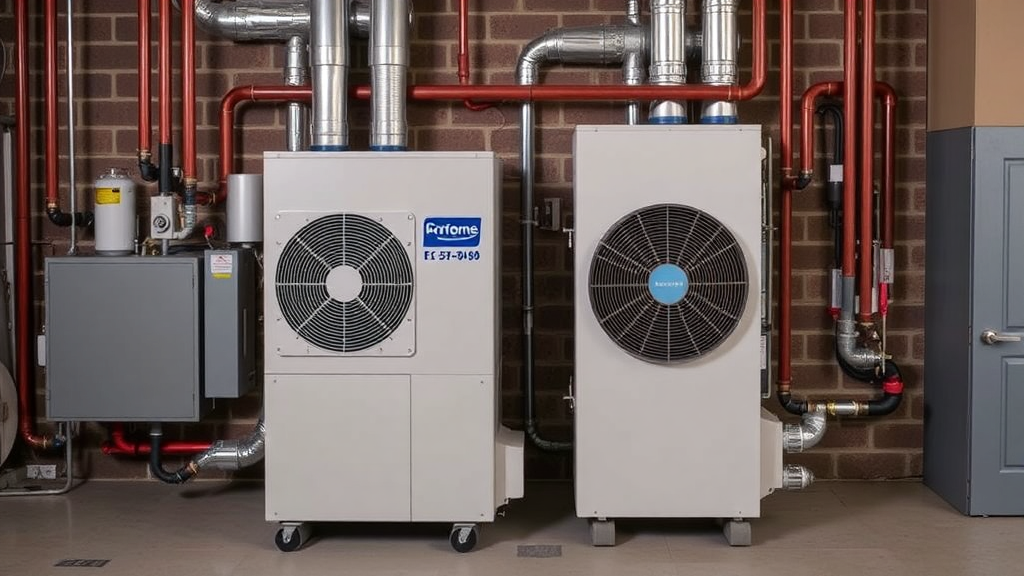
In the world of heating and cooling systems, variable-speed hydronic heat pumps are gaining a solid reputation among contractors for their versatility and efficiency. These innovative systems are designed to optimize energy use, providing significant benefits to both contractors and their clients.
One of the primary advantages of variable-speed hydronic heat pumps is energy efficiency. Unlike traditional systems that operate at a fixed speed, variable-speed pumps adjust their output based on the heating or cooling demand. This capability allows for smoother operation and reduces energy consumption. As a contractor, you can offer your clients a solution that not only saves them money on energy bills but also aligns with environmentally friendly practices.
Another benefit of these heat pumps is their enhanced comfort levels. By providing consistent temperatures and minimizing temperature fluctuations, variable-speed systems improve a home’s comfort. Homeowners particularly appreciate this feature, as it leads to a more pleasant environment year-round. This can be a significant selling point when you’re presenting options to clients.
Variable-speed hydronic heat pumps also contribute to quieter operation. Traditional systems often generate disruptive noise during operation, making them unappealing in residential settings. In contrast, these modern pumps run at lower speeds during milder weather conditions, resulting in significantly less noise. A quieter environment is an attractive feature for homeowners, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction with your services.
Furthermore, these heat pumps are highly scalable. Contractors have the flexibility to install them in various settings, whether in new constructions or retrofitting existing systems. This adaptability opens up new business opportunities and allows you to work with a broader range of clients. Variable-speed hydronic heat pumps are effective in both small homes and larger commercial spaces, which can help you expand your customer base.
With today’s focus on sustainability, variable-speed hydronic heat pumps utilize eco-friendly refrigerants and advanced technology. This aligns with the growing demand for green solutions among consumers. When you promote systems that have a lower environmental impact, you not only appeal to eco-conscious clients but also position yourself as a forward-thinking contractor in an evolving market.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Reduces energy consumption, leading to lower utility bills. |
| Improved Comfort | Provides consistent temperatures with minimal fluctuations. |
| Quiet Operation | Runs quietly, ideal for residential environments. |
| Scalability | Can be installed in various building types and sizes. |
| Sustainability | Utilizes eco-friendly refrigerants and technology. |
Variable-speed hydronic heat pumps into your offerings can significantly enhance your competitive edge. Clients are always looking for reliable and efficient heating solutions. By becoming well-versed in these systems and understanding their benefits, you can instill confidence in your clients that they are making a sound investment.
Additionally, the maintenance requirements for variable-speed hydronic heat pumps are relatively low compared to traditional systems. This means less hassle for homeowners and fewer service calls for contractors. Regular maintenance checks ensure optimal performance, but the overall simplicity of these systems is a win-win for all parties involved. For contractors like you, this translates into more comfortable relationships with your clients, as you facilitate easier upkeep.
As you explore the market for variable-speed hydronic heat pumps, partnering with reputable manufacturers can provide access to resources and support. Organizations like NAHB (National Association of Home Builders) and AHRI (Air-Conditioning, Heating, and Refrigeration Institute) offer valuable insights and educational materials that can help you stay informed and position your business effectively.
The benefits of variable-speed hydronic heat pumps for contractors are substantial. These systems promise energy savings, comfort, quiet operation, and adaptability. By integrating such technologies into your services, you’ll not only increase client satisfaction but also lead the charge toward a more sustainable future in the HVAC industry.
Key Features to Consider When Choosing a Heat Pump
When selecting a heat pump, it’s essential to make an informed decision. You need to consider various features that will enhance the functionality, efficiency, and usability of your heating system. Here are some key features to consider:
Efficiency Ratings
The efficiency of a heat pump is a critical factor. You’ll often encounter two main efficiency ratings: the Coefficient of Performance (COP) and the Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER). COP indicates how much heat energy the system can produce per unit of energy consumed, while SEER measures cooling efficiency. Look for a heat pump with a high rating for optimal performance.
Size and Capacity
Your heat pump’s size matters significantly. If it’s too small, it won’t heat or cool your space adequately. If it’s too large, it can cycle off too quickly, causing energy inefficiency. Conduct a load calculation to determine the ideal capacity you need based on the area and the insulation of your home. Generally, heat pumps are available in various sizes, so you should select one that fits your specific needs.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
The installation process of a heat pump is crucial. Some models may require professional installation due to complex components. Make sure to assess the maintenance needs as well, choosing a model that is easy to service. Regular maintenance is vital to keep your heat pump running efficiently. Check if the manufacturer provides a warranty covering periodic maintenance visits.
Climate Suitability
Consider your local climate when selecting a heat pump. Heat pumps work best in moderate climates but can be less effective in extreme temperatures. For colder areas, look for models specifically designed for low temperatures. You can find energy-efficient models that perform effectively, even when the temperature drops. Details about this can be checked at the EnergyStar website.
Noise Levels
No one wants a noisy heating system. When selecting a heat pump, consider the noise levels. Many manufacturers now offer models with quieter operations. Look for products with low decibel levels to ensure comfort in your home. Reading customer reviews can also give you insights into the noise levels of specific brands and models.
Control Systems
Modern heat pumps often come with smart control systems. These allow you to manage the temperature efficiently through a mobile app or a programmable thermostat. Advanced control options help to monitor energy usage and adjust the settings to ensure maximum efficiency. Look for systems that allow remote management and integration with smart home devices.
Rebates and Incentives
Check for any available rebates or incentives in your area. Many regions offer financial assistance or tax credits for installing energy-efficient systems. Research local utility company programs or federal tax incentives to minimize your costs. Websites like DSIRE can help you find information on incentives.
| Feature | Importance |
|---|---|
| Efficiency Ratings | Determines energy savings |
| Size and Capacity | Affects comfort and efficiency |
| Installation and Maintenance | Impacts long-term ownership costs |
| Climate Suitability | Ensures effective heating/cooling |
| Noise Levels | Enhances living comfort |
| Control System | Improves energy management |
| Rebates and Incentives | Reduces initial costs |
By considering these features, you can choose the right heat pump for your needs. Doing thorough research and comparing various options will ensure you select a unit that keeps your home comfortable while also being energy efficient.
Comparison of Variable-Speed Hydronic Heat Pumps and Traditional Systems
As homeowners increasingly seek energy-efficient solutions for their heating needs, understanding the differences between variable-speed hydronic heat pumps and traditional systems becomes crucial for informed decision-making. This comparison highlights the significant advantages of variable-speed hydronic heat pumps over conventional heating methods, including improved energy efficiency, comfort, and sustainability.
Energy Efficiency
Variable-speed hydronic heat pumps stand out due to their remarkable energy-saving capabilities. Unlike traditional systems that generally operate at a fixed speed, these modern heat pumps adjust their output based on the current heating demand. This variable operation means that they can operate at lower speeds during milder weather, leading to reduced energy consumption.
Key factors of energy efficiency include:
- Heating coefficients: Variable-speed hydronic heat pumps have higher seasonal heating efficiency compared to traditional systems.
- Zoning capabilities: These systems can provide consistent heating in specific areas, preventing energy loss from heating unused spaces.
- Integration with renewable energy: They can seamlessly integrate with solar panels or other renewable sources to maximize energy efficiency.
According to the U.S. Department of Energy, heat pumps can reduce energy usage for heating by approximately 50% compared to traditional electric resistance heating.
Comfort Control
One of the primary issues with traditional heating systems is uneven temperature distribution. Variable-speed hydronic heat pumps enhance comfort by providing consistent heating. They have the ability to maintain comfortable temperatures throughout the home without the common peaks and troughs associated with standard systems.
The benefits of enhanced comfort control include:
- Quieter operation: Variable-speed systems are generally quieter, making them more comfortable for indoor living.
- Customized heating: Homeowners can choose different zones for heating based on preference and usage.
- Variable output: These systems adjust the heating output based on real-time temperature data, ensuring greater consistency and comfort.
Environmental Impact
When considering the environmental ramifications of heating systems, variable-speed hydronic heat pumps primarily excel. As they draw heat from the ground or air, they consume less electricity, resulting in a lower carbon footprint. Traditional systems, often reliant on fossil fuels, are a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions.
Some important points on environmental impact include:
- Lower emissions: Utilizing renewable energy sources decreases reliance on fossil fuels.
- Reduced waste: These pumps are designed for longevity, cutting down on waste compared to traditional systems that may need replacement more often.
- Sustainable energy usage: Variable-speed systems leverage available heat, which can positively affect overall energy consumption and help combat climate change.
Long-Term Savings
Investing in a variable-speed hydronic heat pump can lead to significant long-term savings. While the initial investment may be higher than that of traditional systems, the reduced energy bills and minimal maintenance costs often offset this initial expense. An investment in technology that uses less energy pays for itself over time.
Consider the following aspects of long-term savings:
- Lower running costs: Expect anywhere from 20% to 50% savings on energy bills.
- Increased property value: Homes equipped with efficient heating systems can attract higher resale prices.
- Tax credits and incentives: Many regions offer rebates or tax incentives for installing energy-efficient systems, enhancing affordability.
Ultimately, choosing a heating system is a critical decision homeowners face, and variable-speed hydronic heat pumps present a compelling option with numerous benefits over traditional systems. For more information on energy-efficient heating options, visit Energy.gov and HVAC.com.
Installation Best Practices for Variable-Speed Heat Pumps
Installing a variable-speed heat pump is a complex process that requires careful planning and precision. If you are a contractor looking to ensure a smooth installation, here are some best practices that can guide you through the process and enhance the efficiency of the system.
Understanding the System
Before diving into installation, take the time to understand how a variable-speed heat pump operates. Unlike traditional heat pumps, which turn on and off, variable-speed models adjust their speed to meet heating or cooling demands efficiently. This results in less energy waste and greater comfort.
Site Assessment
Conduct a thorough site assessment to determine the best location for the heat pump. Here are key factors to consider:
- Sun Exposure: Install the heat pump in a location that has adequate sunlight to enhance performance.
- Ventilation: Ensure there is proper airflow around the heat pump to facilitate efficient operation.
- Access for Maintenance: Choose a spot that allows easy access for maintenance and servicing.
Sizing the Equipment
Choosing the correct size for the heat pump is critical. An oversized unit can lead to short cycling, while an undersized unit won’t meet heating or cooling needs. Use the Manual J calculation method for accurate sizing, which takes into account:
- House insulation levels
- Window types and sizes
- Local climate
- Occupancy patterns
Installation Steps
Follow these steps to ensure a successful installation:
- Foundation Preparation: Ensure a solid foundation for the heat pump to prevent vibrations and noise.
- Electrical Connections: Follow local codes for electrical installations. Ensure that the heat pump is connected to a dedicated circuit.
- Piping Connections: Use the correct size and type of refrigerant lines for the system, ensuring that there are no kinks or tight bends.
- Insulation: Insulate the refrigerant lines adequately to prevent energy loss.
Refrigerant Charge
After installation, charge the refrigerant correctly for optimal performance. An improperly charged system can cause efficiency issues and strain the compressor. Always refer to the manufacturer’s specifications for the appropriate refrigerant levels.
System Configuration
Once installed, configuring the thermostat and control settings is critical. Ensure that it’s programmed correctly to take advantage of the variable-speed capabilities. This can be fine-tuned for:
- Energy efficiency
- Comfort levels
- Seasonal adjustments
Testing and Verification
After the installation is complete, conduct comprehensive tests to verify that the system is functioning correctly. This includes:
- Checking the airflow
- Measuring the temperature differentials
- Confirming that the system operates quietly and efficiently
Maintenance Guidelines
Educate homeowners on the importance of regular maintenance to keep the variable-speed heat pump operating efficiently. Recommend a yearly maintenance schedule that includes:
- Checking air filters
- Inspecting coils
- Examining drain lines for blockages
Resources for Further Learning
For additional insights and technical information, contractors might explore resources such as Energy Star, which provides guidelines on high-efficiency systems, or HVAC.com for comprehensive HVAC solutions.
Being well-prepared and educated about installation best practices for variable-speed heat pumps ensures that you’re providing high-quality service as a contractor. Efficient installation not only improves customer satisfaction but also maximizes the performance and lifespan of the equipment.
Understanding Energy Efficiency Ratings and Their Importance
Energy efficiency ratings are crucial in helping consumers make informed decisions about their energy usage and overall impact on the environment. Understanding these ratings can significantly influence your choices regarding appliances, heating, and cooling systems.
When assessing energy efficiency, you will encounter several key ratings. These ratings provide important insights into how efficiently a product or system uses energy. This can lead to reduced utility bills and a lowered carbon footprint. Here’s a breakdown of common energy efficiency ratings:
- Energy Star: Products bearing the Energy Star label meet strict energy efficiency guidelines set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). These products typically save 20-30% more energy than their non-rated counterparts.
- Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER): This ratio measures the efficiency of air conditioning systems. The higher the SEER rating, the more efficient the unit. SEER ratings are measured over an entire cooling season.
- Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE): This rating applies to furnaces and boilers. It indicates how efficiently a heating appliance converts fuel into heat. A higher AFUE percentage means better efficiency.
- Energy Use Classification (EUC): This classification helps understand how much energy an appliance consumes during its use. It’s often represented in kWh per year for electrical appliances.
- Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF): For heat pumps, this rating indicates the efficiency of the unit in heating mode. A higher HSPF means better heating efficiency.
Understanding these ratings is essential not only for cost-saving reasons but also for environmental awareness. Here are some reasons why energy efficiency ratings matter:
- Lower Energy Bills: Higher efficiency ratings typically mean lower operating costs, allowing you to save money on monthly energy bills.
- Environmental Impact: By selecting energy-efficient products, you contribute to reduced greenhouse gas emissions and lower energy consumption, helping the planet.
- Increased Comfort: Efficient systems tend to maintain more consistent temperatures, enhancing your overall comfort in your home.
- Resale Value: Energy-efficient homes often have higher market values. Buyers are more inclined to invest in properties that promise lower operating costs.
Now that you understand the significance of energy efficiency ratings, you may want to apply this knowledge when selecting heating, cooling, or appliance systems for your home. When looking at any new HVAC system, pay attention to the SEER, HSPF, and AFUE ratings. A well-rated system can greatly benefit your home’s energy consumption.
For example, an air conditioner with a SEER rating of 16 will be considerably more efficient than one with a rating of 13. This difference could lead to energy savings that add up over time.
| Rating Type | Description | Typical Efficiency Rating |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Star | Meets EPA’s energy efficiency guidelines | 20-30% more efficient |
| SEER | Measures air conditioning efficiency | 13-25+ |
| AFUE | Measures heating system efficiency | 80-98% |
| EUC | Annual energy consumption measurement | Varies by appliance |
| HSPF | Measures heat pump heating efficiency | 7.7-10+ |
When considering a new purchase, always look for these ratings on the product labels. It pays off in the long run. For comprehensive information regarding energy efficiency and ratings, visit Energy Star or check out the resources provided by Air-Conditioning, Heating, and Refrigeration Institute (AHRI).
Moreover, educating yourself on energy efficiency ratings can go a long way in your quest for cost-effective living and environmental sustainability. Understanding how these ratings work and what they indicate about the energy efficiency of your appliances and heating/cooling systems can help you make smarter choices that benefit both your budget and the planet.
Common Challenges in Implementing Hydronic Heat Pumps
Implementing hydronic heat pumps can be an excellent choice for energy-efficient heating and cooling solutions. However, several challenges can arise during the installation and operation of these systems. Understanding these challenges can help contractors effectively address them, ensuring a smoother installation process and more satisfied customers.
The following are some common challenges faced when integrating hydronic heat pumps:
Site-Specific Limitations
One of the initial challenges is determining the suitability of the site. Factors like available space, soil conditions, and existing infrastructure can significantly impact installation. For instance, if the property has poor drainage or is on a slope, it may complicate the installation process. To overcome this, contractors must conduct thorough site assessments.
Complex Installation Requirements
Hydronic systems often require precise installation techniques to function correctly. This includes the proper placement of pipes, controls, and two-way or three-way valves. If any part is not installed correctly, it can lead to inefficiencies or system failures. Here are the critical installation aspects that need attention:
- Pipe Sizing: Improperly sized pipes can restrict flow and reduce efficiency.
- Insulation: Ensure pipes are adequately insulated to prevent heat loss.
- System Balancing: Balancing the system is crucial for ensuring consistent heating and cooling throughout the building.
Initial Cost Considerations
The upfront costs associated with hydronic heat pumps can be a significant barrier for some homeowners. While the long-term savings on energy bills make these systems financially appealing over time, the initial investment may deter potential customers. Contractors can alleviate financial concerns by explaining available financing options or incentives and clearly communicating the long-term benefits of energy savings.
Regulatory and Compliance Issues
Each region may have different codes and regulations governing the installation of hydronic heat pumps. Navigating local regulations can be daunting and time-consuming. Failing to comply can lead to fines or costly rework. It’s crucial for contractors to stay informed about local building codes and regulations. Additionally, working with experienced consultants can help ensure compliance.
System Maintenance and Complexity
Hydronic heat pump systems can be more complex than traditional heating solutions. This complexity may intimidate homeowners, leading them to delay necessary maintenance. Regular maintenance is essential to keep the system running efficiently and maximize lifespan. To support your clients, you may want to provide a clear maintenance schedule and explain the importance of routine checks, including:
- Checking fluid levels and quality
- Inspecting pump performance
- Ensuring proper functioning of controls and sensors
Noise Concerns
Although hydronic systems are typically quieter than other heating systems, noise can still be a concern for homeowners. Unevenly distributed pressure or air trapped in the system may lead to unwanted sounds, like gurgling or banging. Ensuring proper installation and purging of the system can help minimize these issues. Education on noise-reduction strategies can also reassure clients.
| Challenge | Potential Solutions |
|---|---|
| Site-Specific Limitations | Conduct thorough site assessments before installation. |
| Complex Installation Requirements | Training for contractors on precise installation techniques. |
| Initial Cost Considerations | Discuss financing options and long-term savings. |
| Regulatory Issues | Stay updated on local codes and regulations. |
| System Maintenance | Provide clients with clear maintenance schedules. |
| Noise Concerns | Educate clients on strategies to reduce noise. |
Understanding these challenges and actively working to mitigate them will not only enhance the installation experience but also help build long-lasting client relationships. For additional readings on hydronic heat pump systems and solutions, reach out to resources like Hydronic Heating Association and Energy.gov. Utilizing these insights can lead to more effective contract work and better outcomes for your clients.
Future Trends in Hydronic Heating Technology for Contractors
As the HVAC industry evolves, contractors need to stay ahead of the curve, especially when it comes to hydronic heating technology. This field is experiencing rapid changes driven by advancements in energy efficiency, sustainability, and innovative design. Here are some of the trends shaping the future of hydronic heating technology that every contractor should know.
Smart Hydronic Systems
Smart technology is finding its way into nearly every aspect of our lives, and hydronic heating is no exception. Smart hydronic systems allow for enhanced control and efficiency. Some key features include:
- Remote Monitoring: Contractors can monitor system performance from anywhere, ensuring proactive maintenance and quicker troubleshooting.
- Adaptable Settings: Homeowners can control their heating preferences with user-friendly applications, optimizing comfort and energy use.
- Integration with Smart Home Devices: Systems can easily integrate with existing smart home setups, providing seamless user experience.
Variable-Speed Heat Pumps
Variable-speed heat pumps are becoming increasingly popular due to their energy efficiency and performance capabilities. Unlike traditional single-speed systems that only operate at full capacity or not at all, variable-speed heat pumps adjust their output based on current demand. This results in:
- Improved energy savings due to less energy wasted during operation.
- More consistent temperature levels in the home.
- Quieter operation since the system can run at lower speeds when less heating is required.
Renewable Energy Integration
The growing focus on sustainability is pushing the hydronic heating industry towards incorporating renewable energy sources. A few developments include:
- Solar Thermal Systems: These systems capture sunlight and convert it into heat, which can be used in hydronic heating, reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
- Geothermal Systems: Utilizing the earth’s stable temperatures, geothermal systems are being combined with hydronic heating for maximum efficiency.
- Hybrid Systems: Combining conventional boilers with renewable sources provides flexibility and improved system performance.
Enhanced Insulation Techniques
As energy efficiency becomes paramount, the role of insulation cannot be underestimated. Modern hydronic systems are evolving to work more effectively with improved insulation technologies. Key improvements include:
- Better thermal insulation materials that reduce heat loss within piping and components.
- insulation into hydronic unit designs for greater overall efficiency.
- Utilization of reflective barriers in installations to optimize heat retention.
Focus on Modular Systems
Modular hydronic systems are increasingly in demand due to their flexibility and ease of installation. Advantages of modular systems involve:
- Scalable solutions that allow contractors to customize installations based on specific project needs.
- Reduced installation time due to prefabricated components that are easy to assemble.
- Lowered operational costs as modular systems can operate efficiently in varying conditions.
Advanced Control Systems
Modern hydronic heating solutions are incorporating sophisticated control systems capable of optimizing operations based on real-time feedback. Some advancements include:
- Weather-responsive controls that adjust system parameters based on outside temperature, enhancing comfort.
- Zone control systems that allow for targeted heating in individual rooms, improving comfort while reducing energy waste.
- Data analytics that helps contractors optimize system performance through insights gathered from usage patterns.
Training and Development Opportunities
To effectively integrate these new technologies, continuous training and development for contractors are crucial. Several organizations offer resources and programs, such as:
- National Association of Home Builders – Provides training and knowledge about modern HVAC trends.
- Air-Conditioning, Heating, and Refrigeration Institute – Offers educational materials and certification programs.
- HVAC.com – A great resource for updates and industry insights.
As the industry shifts towards more sustainable and efficient solutions, staying informed about these trends will empower contractors to make better decisions, enhance customer satisfaction, and drive business growth. Understanding advancements in hydronic heating technology is not just important; it is essential for meeting the demands of today’s market.
Key Takeaway:
In today’s fast-evolving HVAC landscape, understanding the ins and outs of Variable-Speed Hydronic Heat Pumps is crucial for contractors aiming to deliver top-notch service to clients. This article highlights several important themes that demonstrate the critical advantages of using these advanced systems.
Firstly, the benefits of Variable-Speed Hydronic Heat Pumps for contractors are substantial. These pumps offer enhanced energy efficiency, which translates to cost savings for clients, and an opportunity for contractors to stand out in a competitive market. Clients appreciate lower utility bills and increased comfort, which can lead to positive reviews and repeat business.
When choosing a heat pump, specific key features need careful consideration. Contractors should prioritize units with variable-speed technology, which allows for more precise temperature control and a quieter operation. Features like smart compatibility and ease of maintenance are also worth noting, as they can simplify installations and enhance customer satisfaction.
Comparatively, Variable-Speed Hydronic Heat Pumps outperform traditional systems in multiple ways. They not only consume less energy but also contribute to improved indoor air quality. The flexibility in operation means they can adapt to varying heating demands more effectively, which is a bonus for any homeowner looking to optimize comfort.
Installation best practices are pivotal when integrating these systems. Proper sizing and placement ensure optimal performance, and contractors should be well-versed in recommended installation guidelines to prevent potential pitfalls. Additionally, understanding energy efficiency ratings is essential. These ratings provide insight into the operational costs and environmental impact of different systems, guiding contractors in making informed recommendations.
However, implementing hydronic heat pumps can present challenges such as system complexity and the need for additional training. Recognizing these hurdles is vital, as it prepares contractors to handle client expectations effectively.
Looking ahead, future trends in hydronic heating technology suggest an increasing focus on smart systems and renewable energy integration. By staying abreast of these trends, contractors can enhance their expertise and offer innovative solutions that meet tomorrow’s heating demands.
Embracing Variable-Speed Hydronic Heat Pumps not only positions contractors as forward-thinking but also equips them with superior tools to enhance customer satisfaction, drive energy efficiency, and face upcoming industry challenges confidently.
Conclusion
As the demand for efficient heating solutions continues to rise, Variable-Speed Hydronic Heat Pumps emerge as a compelling option for contractors looking to provide their clients with high-performance systems. The benefits they offer not only enhance comfort but also significantly improve energy efficiency, translating into cost savings for homeowners. By prioritizing key features such as variable capacity, advanced controls, and compatibility with existing systems, contractors can ensure they select the right heat pump for their projects.
This new technology stands in contrast to traditional heating systems, offering superior adaptability and lower operational costs. Understanding the nuances of installation best practices is crucial for maximizing the performance of these systems. As you integrate Variable-Speed Heat Pumps into your offerings, being aware of energy efficiency ratings can guide you in helping clients make informed choices that align with their sustainability goals.
While adopting such innovative systems may present challenges, like overcoming installation hurdles or addressing consumer education, the long-term benefits far outweigh these initial obstacles. Keeping abreast of future trends in hydronic heating technology positions contractors to remain competitive and responsive in a rapidly evolving marketplace.
By embracing Variable-Speed Hydronic Heat Pumps, you not only enhance your service offerings but also contribute to a more sustainable future in residential heating. Equip yourself with knowledge, stay updated on advancements, and continue to elevate your business by providing clients with state-of-the-art heating solutions. With the right tools and insights, you can lead the way in transforming residential heating into a more efficient and comfortable experience.




Leave a Reply