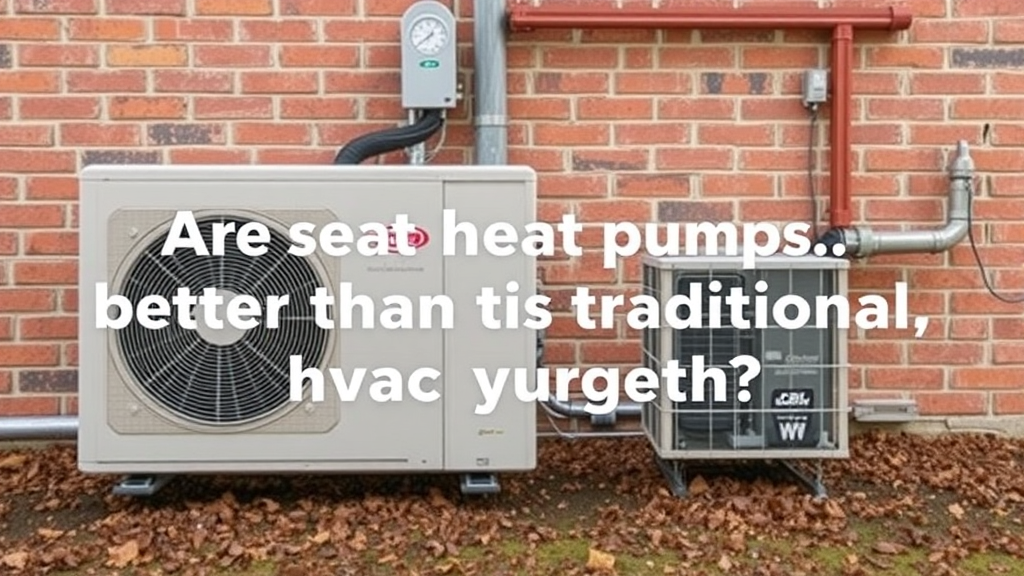
Are heat pumps better than traditional HVAC systems?
Many homeowners face the decision of choosing between heat pumps and traditional HVAC systems. Understanding the differences can help you make an informed choice for your home’s heating and cooling needs. Let’s explore the advantages and disadvantages of both systems.
What is a Heat Pump?
A heat pump is a system that transfers heat from one place to another. It works by utilizing a refrigeration cycle to extract heat from the air, ground, or water, making it versatile for heating or cooling. While heat pumps are often associated with mild climates, they can be effective in various temperatures with the right specifications.
Benefits of Heat Pumps
- Energy Efficiency: Heat pumps consume less energy compared to traditional HVAC systems. They can produce three times more heat energy than the electric energy they consume.
- Environmentally Friendly: By using renewable heat sources, heat pumps have a lower carbon footprint. This makes them a greener option, especially in terms of reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Space Saving: Heat pumps don’t require extensive ductwork, making them ideal for smaller homes or retrofitting older buildings.
- Dual Functionality: Heat pumps can both heat and cool your space. This versatility can be a significant benefit for homeowners seeking year-round comfort.
Disadvantages of Heat Pumps
- Performance in Extreme Cold: While modern heat pumps have improved, extreme cold temperatures can reduce efficiency. Supplemental heating may be needed in such cases.
- Initial Cost: The upfront cost of installing a heat pump can be higher than traditional systems. However, the lower operating costs may offset this expense over time.
- Noise Levels: Some heat pumps can be noisier than traditional HVAC systems, particularly the outdoor units.
Traditional HVAC Systems Explained
Traditional HVAC systems typically include either a furnace or an air conditioner. Furnaces burn fuel or use electricity to heat air, which is then distributed through ductwork, while air conditioners cool air and circulate it back into the home.
Advantages of Traditional HVAC Systems
- Reliable Heating: Furnaces provide heating even in extremely cold weather, which is essential for northern climates where temperatures can plummet.
- Lower Initial Costs: Typically, traditional systems may cost less to install than heat pumps, making them more appealing for those on a budget.
- Proven Technology: Traditional systems have a long history of reliable operation, making many homeowners feel comfortable with their choice.
Drawbacks of Traditional HVAC Systems
- Higher Energy Consumption: They can consume significantly more energy, which may lead to higher utility bills over time.
- Environmental Impact: Fossil fuel-based systems produce greenhouse gases that contribute to environmental degradation.
- Space Requirements: Traditional systems often require extensive ductwork, which may be a limiting factor in some homes.
Making the Right Choice
When deciding whether heat pumps are better than traditional HVAC systems, consider your specific needs, climate conditions, and budget. A thorough analysis can help you weigh the pros and cons effectively.
| Feature | Heat Pumps | Traditional HVAC |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | High | Moderate |
| Environmental Impact | Low | High |
| Performance in Cold | Variable/Supplement needed | Reliable |
| Initial Cost | High | Lower |
Ultimately, the choice between heat pumps and traditional HVAC systems depends on your location, energy preferences, and financial considerations. Evaluate your options and consult with professionals to determine what fits best for your home. For more information on heat pumps and HVAC systems, check out Energy.gov and HVAC.com.
Energy efficiency comparison between heat pumps and traditional units
When it comes to choosing an HVAC system for your home, understanding energy efficiency is crucial. Heat pumps and traditional HVAC systems both provide heating and cooling, but their energy efficiency differs significantly. Knowing how these systems stack up can help you make an informed decision that not only affects your comfort but also your monthly energy bills.
Heat pumps function by transferring heat rather than generating it. In the winter, they extract heat from the outside air or ground and use it to warm your home. In contrast, traditional HVAC systems use combustion or resistance heating to create warmth. This fundamental difference in operation directly impacts energy usage and efficiency.
Here’s a brief overview of the energy efficiency of heat pumps compared to traditional HVAC systems:
| System Type | Energy Source | Average Efficiency (SEER/EER & HSPF) | Cooling Cost (per month)* | Heating Cost (per month)* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heat Pump | Electricity | 15-25 SEER / 8-12 HSPF | $85 | $100 |
| Traditional Central AC | Electricity / Gas | 13-20 SEER | $100 | $120 |
| Traditional Furnace | Gas | 80-98% AFUE | N/A | $150 |
*Costs can vary depending on location, size of the home, and usual climate conditions.
One of the strongest attributes of heat pumps is their energy efficiency ratings. The Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) measures cooling output during a season divided by the total energy consumed. The Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF) does the same for heating. Higher ratings mean better energy efficiency.
On average, modern heat pumps can achieve a SEER rating between 15 and 25, with HSPF ratings ranging from 8 to 12. This means heat pumps can deliver about two to three times more energy in heating or cooling than they consume in electricity. Such high efficiency often translates into lower energy bills.
In contrast, traditional HVAC systems usually feature lower SEER ratings, generally ranging from 13 to 20, with heating systems operating with AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency) rates of 80% to 98%. Essentially, a gas furnace that operates at 90% AFUE wastes about 10% of the energy it consumes for heating. This inefficiency results in higher energy costs, especially during peak usage seasons.
It’s also important to consider the environmental impact. Heat pumps produce significantly less carbon emissions compared to traditional gas furnaces, particularly if powered by renewable energy sources. This makes heat pumps a greener option for energy-conscious homeowners.
However, a heat pump may not always be the best choice in extremely cold climates. While they are effective at moderate temperatures, their efficiency can decline when temperatures drop below freezing. In these situations, homeowners often need a supplemental heating source, which can negate some of the energy savings.
To maximize efficiency regardless of the type, regular maintenance is essential. Ensure your HVAC system is serviced at least once a year. This helps keep it running smoothly and efficiently. You can find more information about proper maintenance at Energy Star and stay updated on tips for improving energy efficiency.
Heat pumps generally provide higher energy efficiency compared to traditional HVAC systems, translating to lower utility costs and reduced environmental impact. However, factors such as climate, home size, and your specific energy needs will ultimately guide your final decision. Take time to weigh your options and consult with an HVAC professional to determine the ideal system for your unique situation.
The long-term cost benefits of installing a heat pump
When considering a new HVAC system for your home, the long-term cost benefits of installing a heat pump can be a significant factor in your decision-making process. Heat pumps operate differently compared to traditional heating and cooling systems, which allows them to offer unique financial advantages over time.
One of the standout features of heat pumps is their energy efficiency. They transfer heat instead of generating it directly, making them considerably more efficient than traditional systems. For instance, a heat pump can deliver up to three times more heating or cooling energy than the electrical energy it consumes. This efficiency translates into lower energy bills, often saving homeowners up to 50% on their heating and cooling costs.
How Heat Pumps Save Money Over Time
The long-term savings with heat pumps can be attributed to several key factors:
- Reduced Energy Consumption: As mentioned, heat pumps use significantly less energy. This efficiency not only cuts monthly utility bills but also conserves natural resources.
- Lower Maintenance Costs: Heat pumps typically require less maintenance than traditional HVAC systems. With fewer moving parts and no need for fuel deliveries, homeowners may find themselves spending less on repairs and upkeep.
- Longer Lifespan: A well-maintained heat pump can last 15-20 years, which is often longer than traditional systems. This longevity reduces the frequency of replacements, spreading out costs over a longer period.
- Potential Rebates and Tax Incentives: Many local governments and utility companies offer rebates and tax cuts for installing energy-efficient systems like heat pumps. Homeowners can take advantage of these programs to offset initial installation costs.
For instance, many residents in areas with government incentives have reported significant savings when switching to heat pumps. These initial incentives can sometimes cover a sizable portion of installation costs. If you’re curious about local energy savings programs, resources like Energy.gov provide information and guidance on potential savings in your area.
Heat Pump Performance and Comfort
Another aspect that contributes to the long-term cost benefits is the comfort and performance of heat pumps. Unlike traditional systems, heat pumps are known for their ability to maintain consistent temperatures without the spikes often associated with traditional furnaces or air conditioners.
This steady performance can lead to additional cost savings. For example, by avoiding temperature fluctuations, you reduce the stress on your system, potentially extending its lifespan. Furthermore, more comfortable homes often lead to less energy being used for heating adjustments, reducing overall consumption.
Cost Comparison with Traditional HVAC Systems
To give you a clearer picture of the long-term costs associated with heat pumps versus traditional HVAC systems, consider the following table:
| Feature | Heat Pump | Traditional HVAC |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency Rating (SEER) | 15-25 | 8-14 |
| Average Lifespan | 15-20 years | 10-15 years |
| Maintenance Costs | Lower | Higher |
| Energy Savings (compared to traditional system) | 30-50% | – |
As the table illustrates, heat pumps trump traditional HVAC systems in multiple areas, particularly in lifecycle efficiency and long-term savings. Over time, the cumulative savings from energy efficiency and reduced maintenance can add up significantly.
Environmental Impact
In addition to financial savings, heat pumps have a positive impact on the environment. By using less energy, they help to lower greenhouse gas emissions. Homeowners making the switch to heat pumps aren’t just saving money; they’re also making a more sustainable choice.
For those looking to invest in an HVAC system that balances efficiency, cost savings, and environmental benefits, heat pumps clearly stand out as an excellent option. To further enhance your understanding of heat pumps and to find local installation assistance, visit Energy Star’s heat pump section.
Environmental impact: Heat pumps vs. conventional HVAC systems
When considering heating and cooling solutions for your home or business, evaluating the environmental impact is crucial. Heat pumps and traditional HVAC systems operate significantly differently, and understanding these differences can help you make an informed decision. Let’s explore the environmental aspects of both systems.
Heat pumps operate by transferring heat rather than generating it. In the winter, they extract heat from the outside air, ground, or water and pump it indoors. In contrast, traditional HVAC systems, like furnaces, burn fossil fuels to create heat or utilize electrical resistance heating. This fundamental difference is key to understanding their environmental footprints.
One of the main advantages of heat pumps is their energy efficiency. On average, heat pumps can produce three to four units of heat for every unit of electricity consumed. This high efficiency not only reduces your energy bills but also results in lower carbon emissions compared to conventional HVAC systems. Traditional systems, particularly those using oil or gas, can emit significant amounts of greenhouse gases. For instance, a gas furnace emits approximately 1.2 to 1.3 tons of CO2 for every 1,000 therms of energy produced. In contrast, heat pumps can help cut these emissions significantly.
Another aspect to consider is the type of energy that powers the systems. Heat pumps can be powered by renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind. If you couple a heat pump with solar panels, you can create a sustainable loop that minimizes reliance on fossil fuels. Conversely, traditional HVAC systems depend heavily on fossil fuels, which not only contributes to greenhouse gas emissions but also depletes non-renewable resources.
Moreover, heat pumps tend to have a lower impact on local environments. Traditional systems may require extensive ductwork or outdoor units that can disrupt habitats. In contrast, many heat pump models are designed with compact sizes and can be installed in ways that preserve landscaping and local ecosystems. This makes them a more environmentally friendly option for installations in sensitive areas.
Efficiency also extends to operating costs. While the initial investment for heat pumps can be higher than traditional HVAC systems, they lead to long-term savings. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, homeowners can expect to save up to 50% on heating and cooling costs with heat pumps. As energy prices continue to rise, the financial benefits of heat pumps become even more compelling.
However, there are considerations to be aware of. In extremely cold climates, heat pumps may struggle to function efficiently. Most advanced models operate well in temperatures as low as -5°F, but performance can dip in harsh winters. Traditional systems may still be necessary in these cases, often resulting in higher environmental impacts during prolonged use.
When comparing heat pumps to conventional HVAC systems, it’s essential to look at the whole lifecycle of the equipment. The manufacturing process, longevity, and end-of-life disposal can all impact the environment. Heat pumps generally have a longer lifespan than traditional systems, averaging 15-20 years, compared to 10-15 years for conventional units. A longer operational lifespan means fewer resources expended on replacements.
Heat pumps present numerous environmental advantages over traditional HVAC systems:
- Energy Efficiency: Up to three to four times more efficient.
- Lower Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Significantly reduced CO2 emissions.
- Utilization of Renewable Energy: Compatible with solar and wind energy sources.
- Reduced Habitat Disruption: More compact installation options.
- Longer Lifespan: Typically lasts longer than traditional systems.
While there are situations where traditional HVAC systems are still prevalent, the environmental benefits of heat pumps make them a compelling choice for modern heating and cooling. For further reading on heat pumps and their benefits, visit Energy Saver for comprehensive information.
How climate affects the performance of heat pumps and HVAC systems
When considering heating and cooling options for your home, understanding how climate affects the performance of heat pumps and HVAC systems is crucial. Depending on where you live, these systems can operate quite differently. Let’s explore these impacts to help you make a more informed decision.
Heat Pump Performance Across Different Climates
Heat pumps work by transferring heat rather than generating it through fuel combustion. This efficiency is most pronounced in moderate climates. However, the performance of heat pumps can experience challenges in extreme conditions. Here’s how various climates impact heat pump efficiency:
- Moderate Climates: Heat pumps thrive in regions with mild winters and moderate summers. They can efficiently heat and cool homes without requiring supplementary systems.
- Cold Climates: In areas where temperatures drop significantly, heat pumps lose efficiency. As the temperature decreases, they struggle to extract enough heat from the outside air. This can necessitate backup heating sources, often increasing energy costs.
- Hot Climates: In hotter areas, heat pumps can efficiently cool homes. However, their effectiveness may dwindle during prolonged heat waves, leading to issues such as frequent cycling, where the system turns on and off more often than it should.
Understanding HVAC System Efficiency in Various Conditions
Traditional HVAC systems, which often rely on furnaces and air conditioners, also react differently based on climate:
- Heat-Only Regions: In places where winter temperatures drop dramatically, traditional heating systems tend to perform reliably, providing consistent warmth without the efficiency concerns faced by heat pumps.
- Dual-Climate Areas: Regions that experience both hot summers and cold winters benefit from HVAC systems that can efficiently manage both heating and cooling. However, their efficiency depends on the type of unit and the local climate.
- Humid Climates: In high humidity areas, HVAC systems may struggle to keep indoor temperatures comfortable while regulating moisture levels. This could lead to mold issues and high electricity bills due to constant operation.
Energy Efficiency Ratings
When comparing heat pumps and HVAC systems, it’s essential to consider the energy efficiency ratings. The Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) for cooling and the Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF) for heating are critical metrics. Generally, heat pumps have higher SEER ratings, often between 14 and 23, compared to traditional HVAC systems. This can make heat pumps a more attractive option in regions where energy efficiency is a priority.
| System Type | Average SEER Rating | Average HSPF Rating |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Pump | 14 – 23 | 8 – 10 |
| Traditional HVAC System | 14 – 20 | 8 – 9 |
Climate Adaptations for Optimal Performance
To optimize the performance of both heat pumps and traditional HVAC systems based on your climate:
- Choose the Right System: Consider a heat pump if you live in a moderate climate, while a traditional HVAC system might be better for extreme conditions.
- Insulation Matters: Proper insulation will enhance the efficiency of any system. Ensure your home is well-insulated to minimize heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer.
- Regular Maintenance: Regular check-ups can ensure both heat pumps and HVAC systems operate efficiently, irrespective of climate conditions.
- Upgrade Options: Newer models of both systems often incorporate advanced technology to adapt to weather changes. Invest in up-to-date systems for better performance.
Climate plays a significant role in how both heat pumps and traditional HVAC systems perform. These factors impact not only efficiency but also your energy bills and comfort level indoors. Making an informed decision about which system to choose can lead to significant long-term benefits. To explore different heating and cooling options further, you can visit Energy Star and AHRI for comprehensive insights on HVAC effectiveness based on climate.
Maintenance requirements for heat pumps compared to traditional systems
Understanding the maintenance requirements for heat pumps and comparing them to traditional HVAC systems is essential for homeowners considering their options. Both systems require upkeep, but the specifics can differ greatly. Here is a detailed look at how each system fares in terms of maintenance.
Heat Pumps Maintenance Requirements
Heat pumps are known for their energy efficiency, but they still require regular maintenance to operate effectively. Here are some key maintenance tasks associated with heat pumps:
- Regular Filter Changes: Just like traditional HVAC systems, heat pumps have air filters that need to be replaced or cleaned every 1-3 months depending on usage and the environment. This helps maintain air quality and system efficiency.
- Checking Refrigerant Levels: Heat pumps rely on refrigerant to transfer heat, and low levels can hinder performance. Annual checks by a professional can prevent inefficient operation.
- Coil Cleaning: The evaporator and condenser coils can accumulate dirt and debris, which reduces efficiency. Cleaning these coils at least once a year is crucial.
- Insulation Checks: Proper insulation around ducts and piping helps maintain efficiency. Inspecting and repairing any damage can make a significant difference in performance.
- Electrical Connection Maintenance: Annual inspections of connections, capacitors, and relays are also important to ensure the heat pump functions safely and effectively.
Traditional HVAC Systems Maintenance Requirements
Traditional HVAC systems, which typically include furnaces and air conditioners, also have specific maintenance needs. Here are the main tasks needed to keep these systems running smoothly:
- Regular Filter Changes: Like heat pumps, HVAC systems require regular filter maintenance. Monthly checks and changes during peak usage seasons are ideal for maintaining air quality and efficiency.
- Annual System Inspections: Professional inspections at least once a year can help detect HVAC issues before they escalate, ensuring that the system runs efficiently.
- Cleaning Outdoor Units: For air conditioners, clearing debris from outdoor units helps maintain airflow and efficiency.
- Duct Maintenance: Duct cleaning should be scheduled every few years to prevent the build-up of dust and allergens, which can impact the efficiency and air quality of the HVAC system.
- Checking Thermostats: Ensuring that thermostats are calibrated and working correctly can improve energy efficiency and comfort levels in your home.
Side-by-Side Comparison of Maintenance Requirements
| Maintenance Task | Heat Pumps | Traditional HVAC |
|---|---|---|
| Filter Changes | Every 1-3 months | Every 1-3 months |
| Refrigerant Checks | Annual by a professional | N/A |
| Coil Cleaning | Once a year | N/A (only coils in AC systems) |
| Annual Inspections | Recommended | Mandatory |
Cost Considerations
Another consideration when looking at maintenance is cost. While heat pumps generally have fewer moving parts and may cost less in service bills due to their efficiency, they can be more expensive upfront. Traditional HVAC systems, particularly older models, may incur higher maintenance costs due to frequent repairs or replacements of worn-out parts.
Homeowners can significantly benefit from establishing a maintenance schedule for either system, ensuring longevity and reducing unexpected repair costs. For those uncertain about their HVAC maintenance needs, consulting with professionals from reputable sources like Energy Saver can provide valuable insights.
Understanding the maintenance requirements for heat pumps compared to traditional HVAC systems can help you make an informed decision for your home. By adhering to maintenance schedules and ensuring regular inspections, both options can operate efficiently, ultimately saving you money in the long run.
Consumer experiences: Testimonials on heat pumps and HVAC performance
Heat pumps and traditional HVAC systems both play important roles in heating and cooling our homes, but consumer experiences tell an interesting story about their performance and advantages. Many homeowners are beginning to share their first-hand accounts of how these systems meet their needs, which can be helpful for others considering a switch or installation.
One common sentiment is about energy efficiency. Consumers frequently mention that heat pumps have lower operating costs compared to traditional HVAC systems. Homeowners in moderate climates, where temperatures don’t drop too low, report substantial savings on their electricity bills. A survey from the U.S. Department of Energy indicates that heat pumps can reduce energy use for heating by approximately 50% compared to electric resistance heating systems.
In terms of comfort, many testimonials highlight the consistent temperatures maintained by heat pumps. Unlike traditional systems, which can create hot and cold spots, heat pumps often provide a more uniform heating and cooling experience throughout the home. One homeowner in North Carolina shared, “Since switching to a heat pump, I noticed that every room in my house stays consistently warm in the winter. There are no cold drafts anymore!”
Installation experiences vary, but many consumers report that heat pumps can be less invasive to install than ducted traditional HVAC systems. Customers appreciate the flexibility of having ductless options available. For instance, a homeowner in California noted, “The ductless heat pump units were easy to install and didn’t require extensive remodeling. I could have comfort in my home without breaking down the walls!” This makes heat pumps a great option for retrofits in older homes lacking ductwork.
Another benefit mentioned by users is the dual functionality of heat pumps. Many models not only heat but also cool. In areas where both heating and cooling are required, homeowners can appreciate the convenience and cost savings of operating one system instead of two. A resident from Texas stated, “Switching to a heat pump has allowed me to cool my home in the summer without the additional cost of running two separate units.”
Consumer experiences also highlight the environmental impact of heat pumps. With rising concerns about climate change, many homeowners are drawn to the eco-friendliness of this technology. Since heat pumps transfer heat rather than generate it via combustion, users feel they are contributing to a greener planet. A customer from Vermont expressed, “Knowing that my heat pump reduces my carbon footprint gives me peace of mind, especially when heating my home during those long winters.”
Despite these positive experiences, some consumers still express concerns. A few people mentioned that heat pumps may struggle in extremely cold temperatures. In such cases, they sometimes require supplemental heating, which can add to the energy costs. As one homeowner in Minnesota pointed out, “While my heat pump is wonderful most of the winter, there are a few weeks I have to rely on my gas furnace to keep my house warm.”
| Factors | Heat Pumps | Traditional HVAC Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | High (up to 50% savings) | Lower |
| Comfort Level | Consistent temperatures | Possible hot/cold spots |
| Installation | Less invasive (ductless options) | More invasive (ducted systems) |
| Functionality | Heats and cools | Primarily heating or cooling |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint | Higher carbon footprint |
Your choice between heat pumps and traditional HVAC systems ultimately depends on your individual needs, lifestyle, and local climate. For those who prioritize energy efficiency and environmental impact, testimonials consistently favor heat pumps. However, understanding the nuances of each system’s performance can help you make a well-informed decision.
For more detailed insights and expert opinions, consider checking out resources from Energy Star and HVAC.com, which provide helpful information on the latest advancements in heating and cooling technologies.
Key Takeaway:
When considering whether heat pumps are better than traditional HVAC systems, it’s crucial to evaluate several key factors. First and foremost, energy efficiency is a significant area where heat pumps typically outperform traditional units. Heat pumps can transfer heat rather than generate it, making them a more eco-friendly option. This efficiency leads to lower energy bills, which contributes to long-term cost savings. Although the initial investment for a heat pump may be higher, the overall operational cost remains lower due to reduced energy consumption.
Another essential aspect to consider is the environmental impact. Heat pumps have a much lower carbon footprint compared to conventional HVAC systems that rely on fossil fuels. By opting for a heat pump, you not only support the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions but also align yourself with a growing trend toward sustainable living. This greater environmental consciousness can appeal to many consumers looking to make more responsible choices for their homes.
Climate plays a significant role in the performance of heat pumps versus HVAC systems. While heat pumps work efficiently in moderate climates, they may struggle in extreme cold or heat. In contrast, traditional HVAC systems often perform consistently regardless of the weather. Therefore, understanding your local climate is essential when deciding which system is best for you.
Maintenance requirements also differ between heat pumps and traditional systems. Heat pumps typically require less maintenance and fewer repairs, translating into further savings over time. However, they do require specific care, such as routine checks for refrigerant levels and cleaning of filters.
Consumer experiences can provide insight into the performance of both systems. Many users report higher satisfaction levels with heat pumps due to their efficiency and comfort, while others express concerns over their performance in extreme weather conditions.
While both heat pumps and traditional HVAC systems have their respective advantages and challenges, heat pumps often emerge as the more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly option, particularly in suitable climates. Consumers should weigh these factors carefully and consider their specific needs for optimal home comfort and savings.
Conclusion
Choosing the right heating and cooling system for your home can significantly impact both your wallet and the environment. Heat pumps emerge as a strong contender when compared to traditional HVAC systems, especially in energy efficiency. They utilize renewable energy from the air or ground, offering greater efficiency that translates to lower monthly utility bills. Over time, the long-term cost benefits of switching to a heat pump can be substantial, even if the initial investment is higher.
Environmental considerations also favor heat pumps. With lower greenhouse gas emissions and a reduced carbon footprint, these systems contribute to a more sustainable future. However, their effectiveness can vary based on climate. In milder areas, heat pumps truly shine, while traditional HVAC systems may better handle extreme weather conditions.
Maintenance is another critical factor. Heat pumps tend to require less frequent servicing than traditional units, which can lead to further savings in time and money. Many consumers report positive experiences with heat pumps, pointing out their quiet operation and consistent comfort levels.
Ultimately, the decision between heat pumps and traditional HVAC systems hinges on your specific needs, climate, and priorities. By weighing these important aspects, you can make an informed choice that not only enhances your home’s comfort but also aligns with your long-term financial and environmental goals. Transitioning to a heat pump may very well be a decision that benefits both you and the planet for years to come.





Leave a Reply